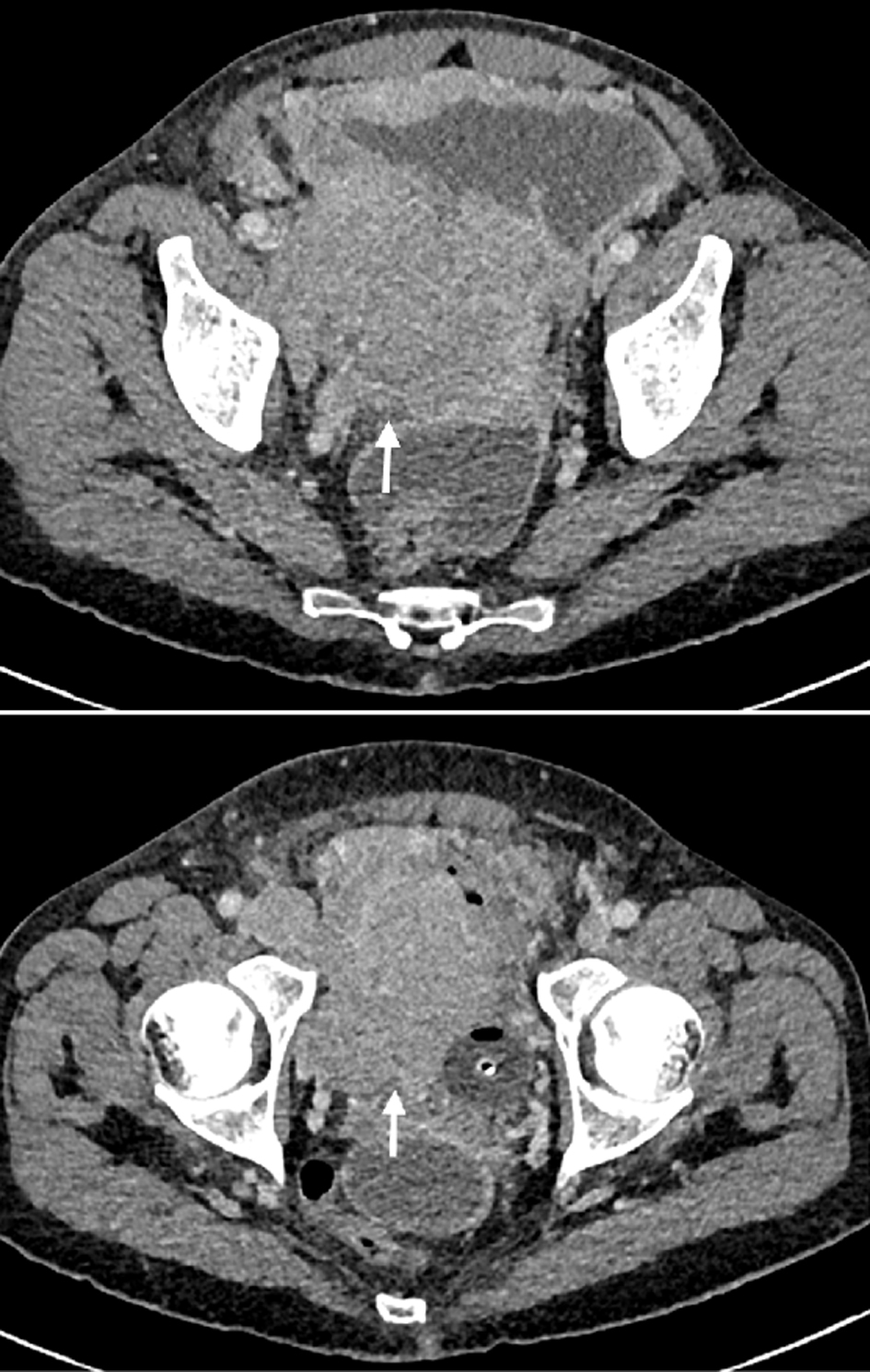
Figure 1. Abdominopelvic CT scan displaying a solid polylobulated retroperitoneal mass which invades the bladder wall, measuring approximately 10 × 10 centimeters. CT: computed tomography.
| Journal of Hematology, ISSN 1927-1212 print, 1927-1220 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Hematol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.thejh.org |
Case Report
Volume 10, Number 1, February 2021, pages 30-34
Spontaneous Tumor Lysis Syndrome: A Rare Presentation in Plasmablastic Lymphoma
Figures

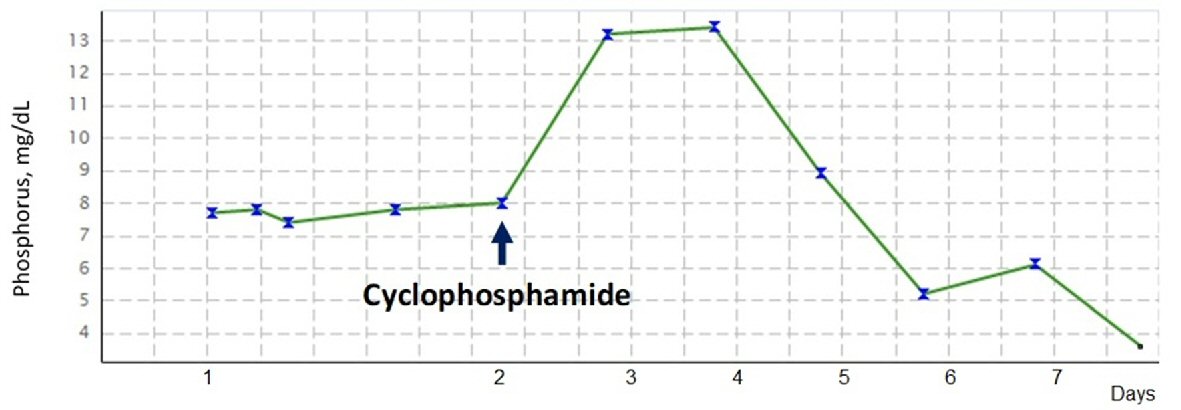
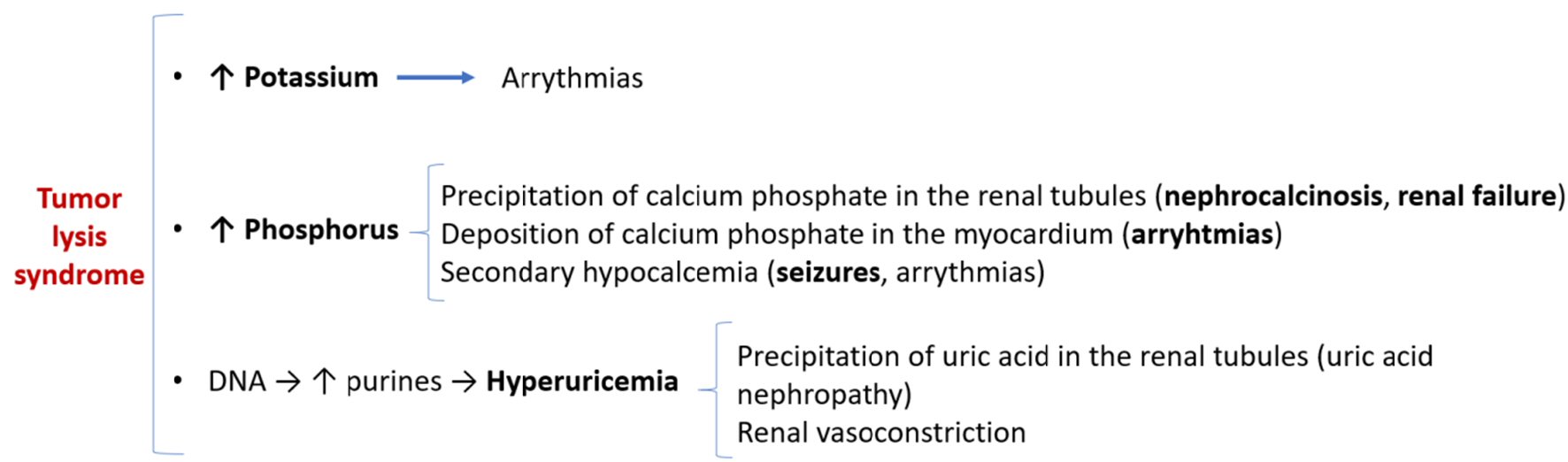
Tables
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Hb: hemoglobin; WBC: white blood count; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase. | |
| Hb | 11.5 g/dL |
| WBC | 5.39 × 109/L |
| Platelets | 307 × 109/L |
| BUN | 90 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 14.03 mg/dL |
| Na+ | 138 mmol/L |
| K+ | 6.6 mmol/L |
| Cl- | 107 mmol/L |
| LDH | 2,012 UI/L |
| Uric acid | 24.9 mg/dL |
| Phosphorus | 7.7 mg/dL |
| Calcium | 8.5 mg/dL |
| TLS: tumor lysis syndrome; WBC: white blood count; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; ULN: upper limit of normal. |
| Tumor-related factors |
| High proliferative rate |
| Chemosensitive tumor |
| High tumor burden |
| Bulky disease (node >10 cm) |
| WBC > 50,000/µL |
| LDH elevation twice the ULN |
| Organ involvement |
| Extensive marrow infiltration |
| Patient-related factors |
| Pre-treatment hyperuricemia or hyperphosphatemia |
| Pre-existing nephropathy |
| Oliguria |
| Dehydration or volume depletion during treatment |