Figures
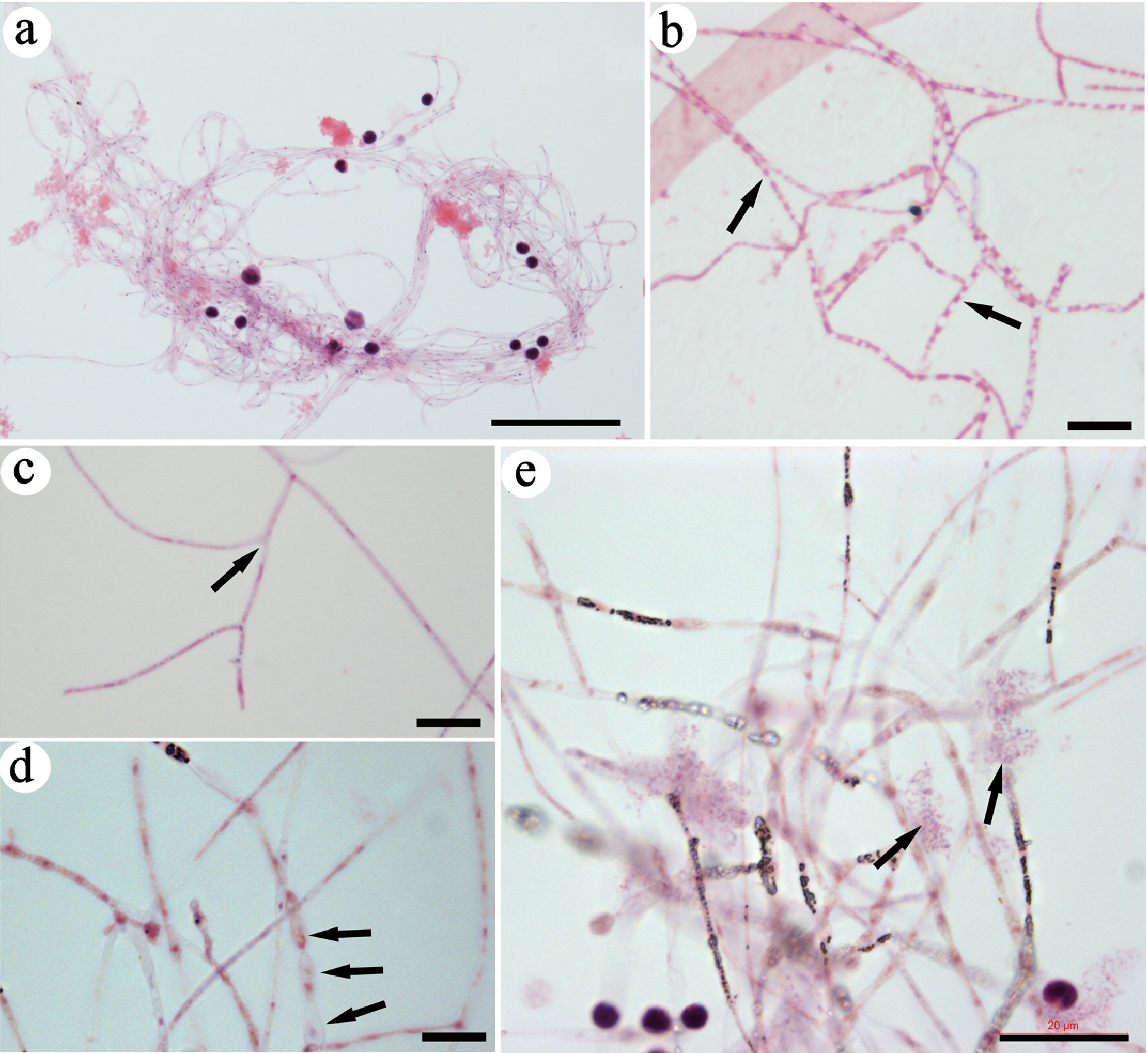
Figure 1. Identifying CRFs in mouse blood. Slides were stained with H&E. A group of CRFs was identified and imaged under lower magnification (a). High-magnification images revealed small eosin-stained materials in the lumen of each filament (arrows in b), filaments with branches (arrows in c), and filaments that were wider and had nodes (arrows in d). Grouped DNA fragments (arrows in e) were located close to the filaments. Bar in a = 50 µm; in b-d = 10 µm; in e = 20 µm. CRF: progenitor-releasing filament; H&E: hematoxylin and eosin.
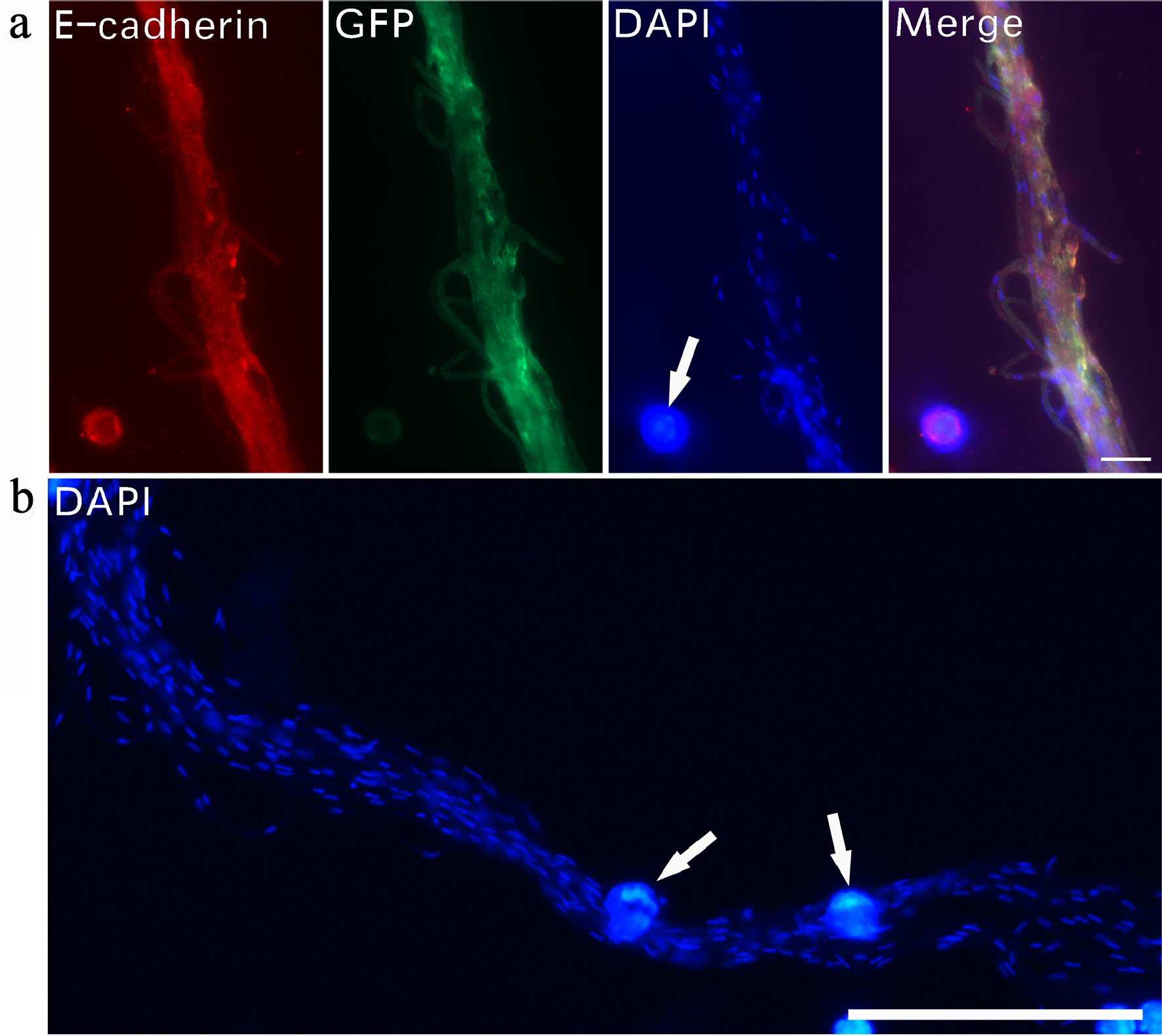
Figure 2. Tiny dot-like DNA in the lumen of filaments. Immunofluorescent staining was used to examine DNA expression in CRFs. A bundle of filaments stained with E-cadherin, GFP and DAPI (a). DAPI staining revealed numerous small nucleus-like DNA dots along a group of bundled filaments (b). Regular-sized cell nuclei (arrows in a, b) are included for size comparison. Bar in a = 10 µm; in b = 50 µm. CRF: progenitor-releasing filament; GFP: green fluorescent protein; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
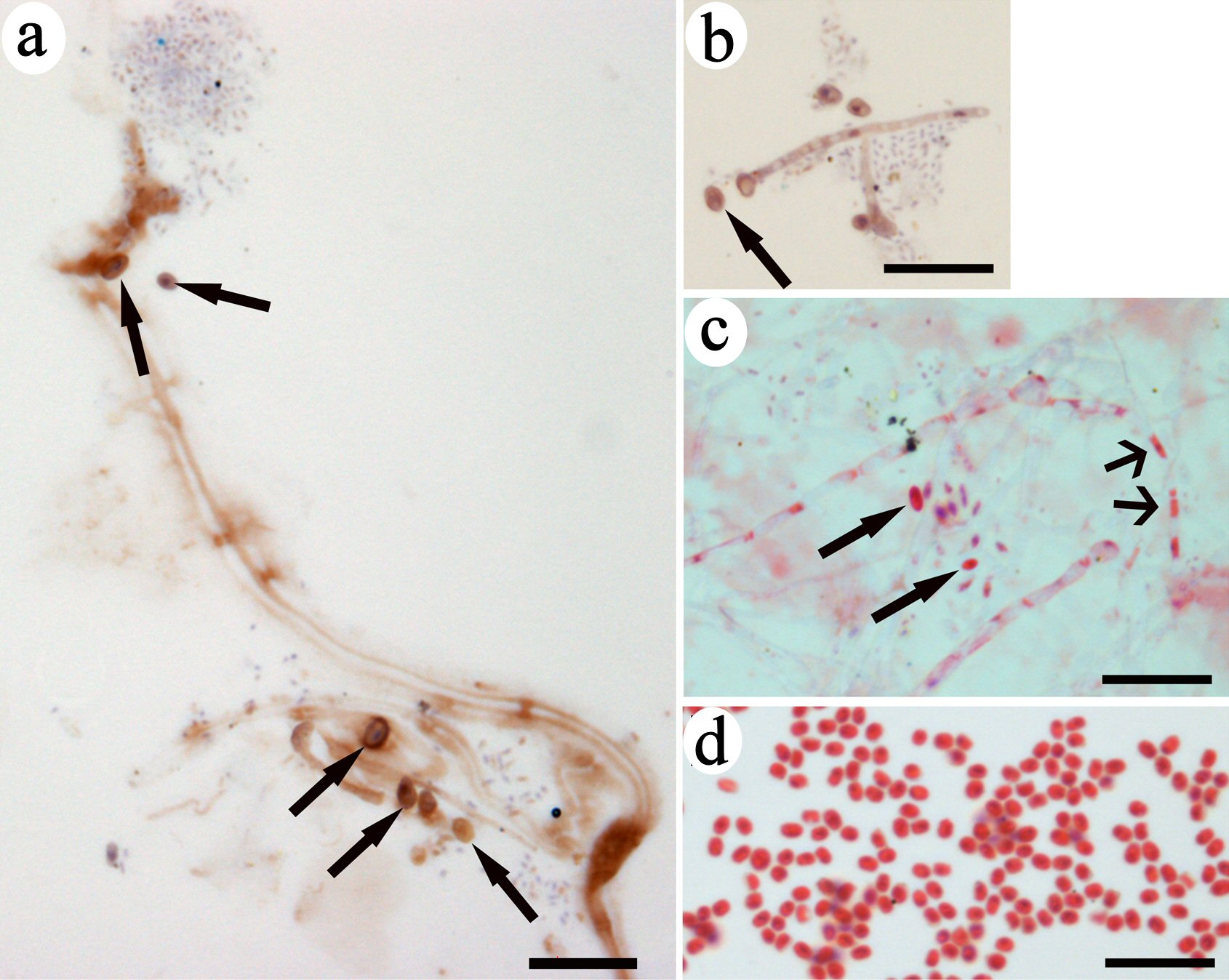
Figure 3. Spore-like small progenitors were released from CRFs. Immunohistochemistry of brown-colored DAB staining indicated CD34 expression on filaments and small progenitors (arrows in a, b). A group of small red-colored progenitors located near the filament with nodes had the same color as the inclusion in the lumen (wide-head arrows in c). One small progenitor (arrow in c) had the same morphology as the small eosin-stained progenitors in (d). Bars = 10 µm. CRF: progenitor-releasing filament; DAB: diaminobenzidine; CD: cluster of differentiation.
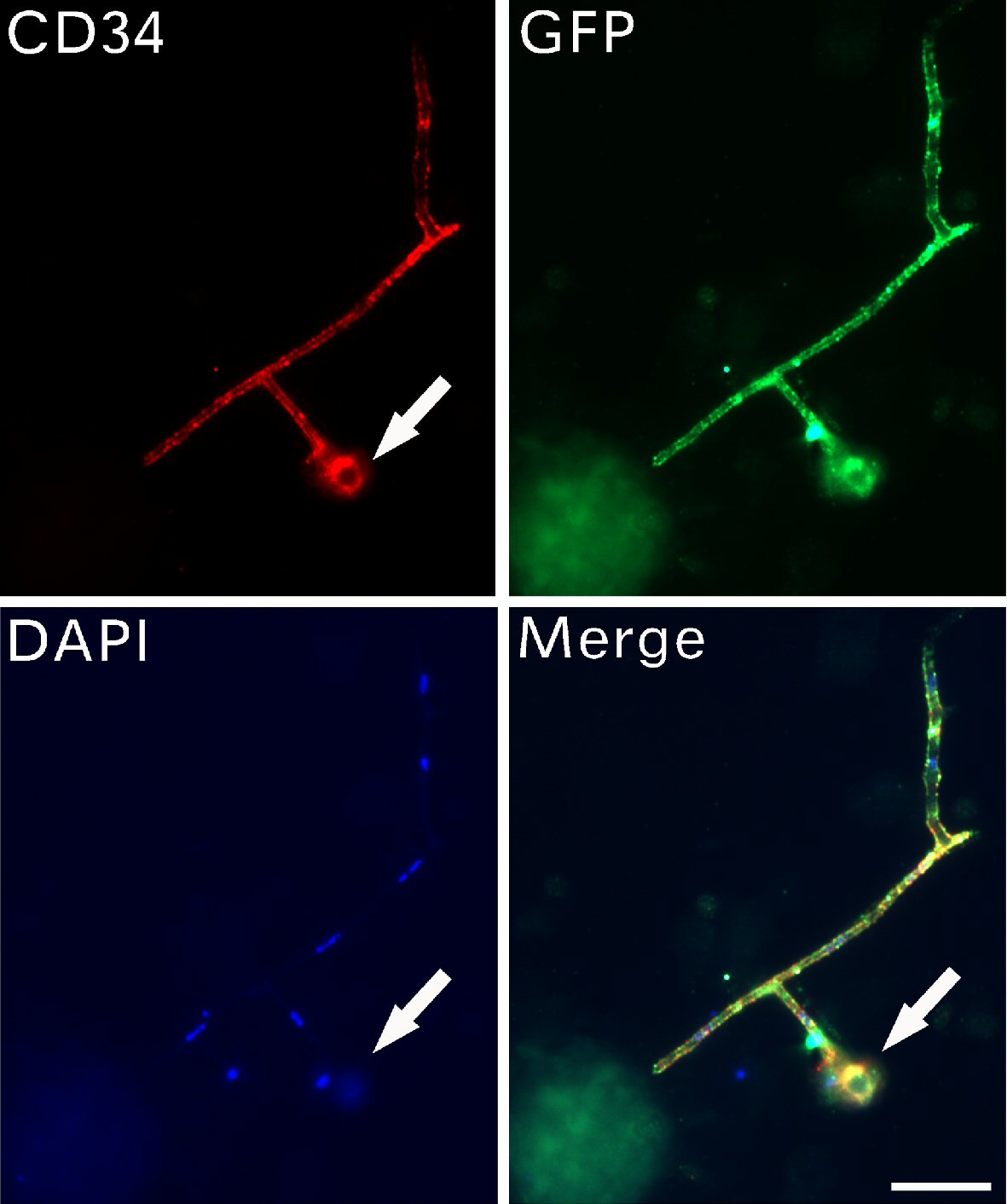
Figure 4. CD34-positive progenitors were larger after release. Immunofluorescent assays detected the expression of CD34, GFP and DAPI on filaments with branches. A small stem cell progenitor (arrows) located at the tip of the filament. Bar = 10 µm. CD: cluster of differentiation; GFP: green fluorescent protein; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
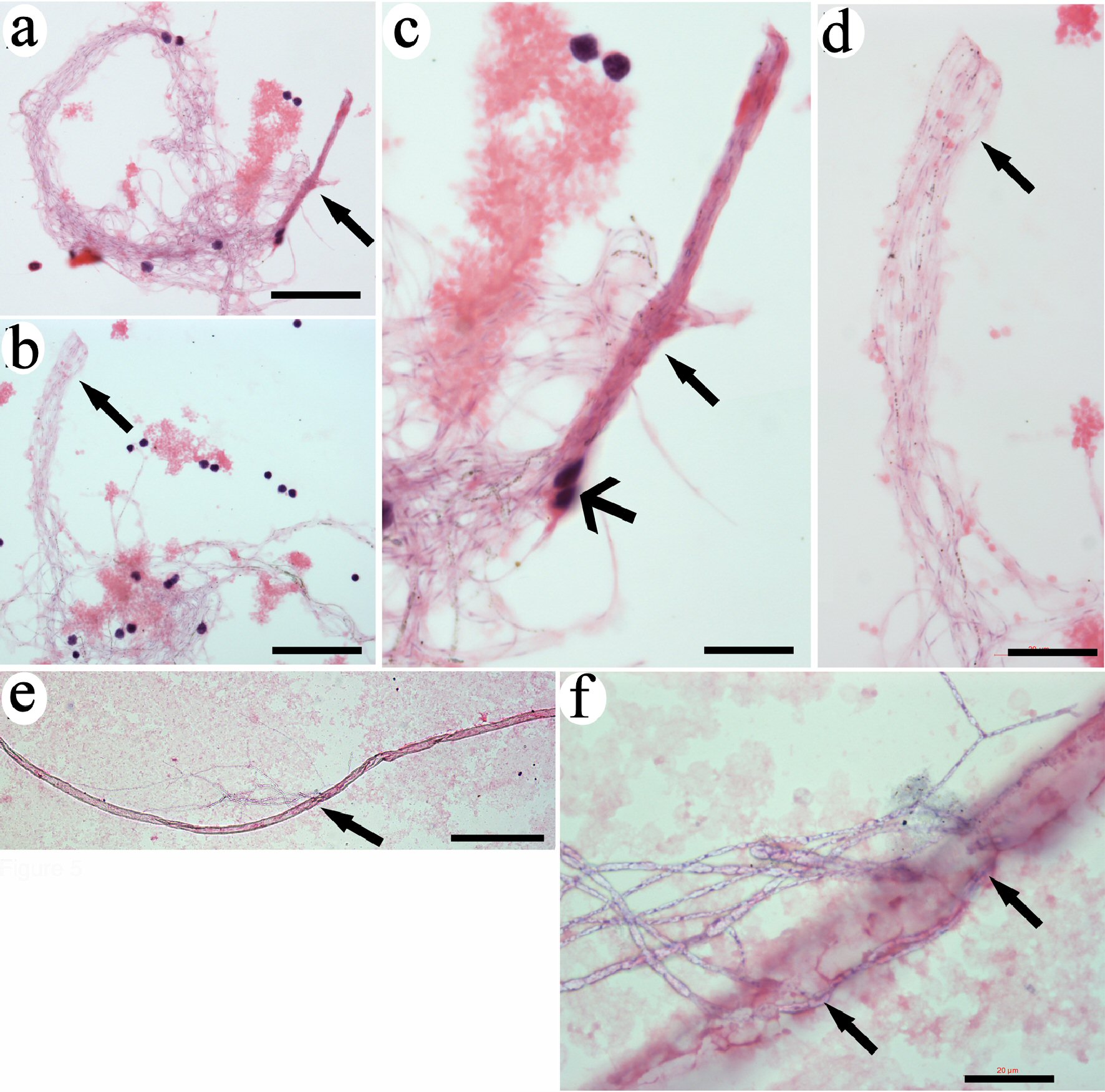
Figure 5. CRFs were originally released from tube-like structures. The ends of tightly bundled filaments were even and with the same length (arrows in a and b). High magnification revealed that the filaments were identical (arrows in c and d). Two monocytes were tightly attached to the filaments (wide-head arrows in c). A long tube-like structure was detected (e). High magnification revealed that filamentary structures were released from the opening in the middle of the tube (arrows in f). Bars in a, b = 50 µm; in c = 10 µm; in d, f = 20 µm; in e = 200 µm. CRF: progenitor-releasing filament.
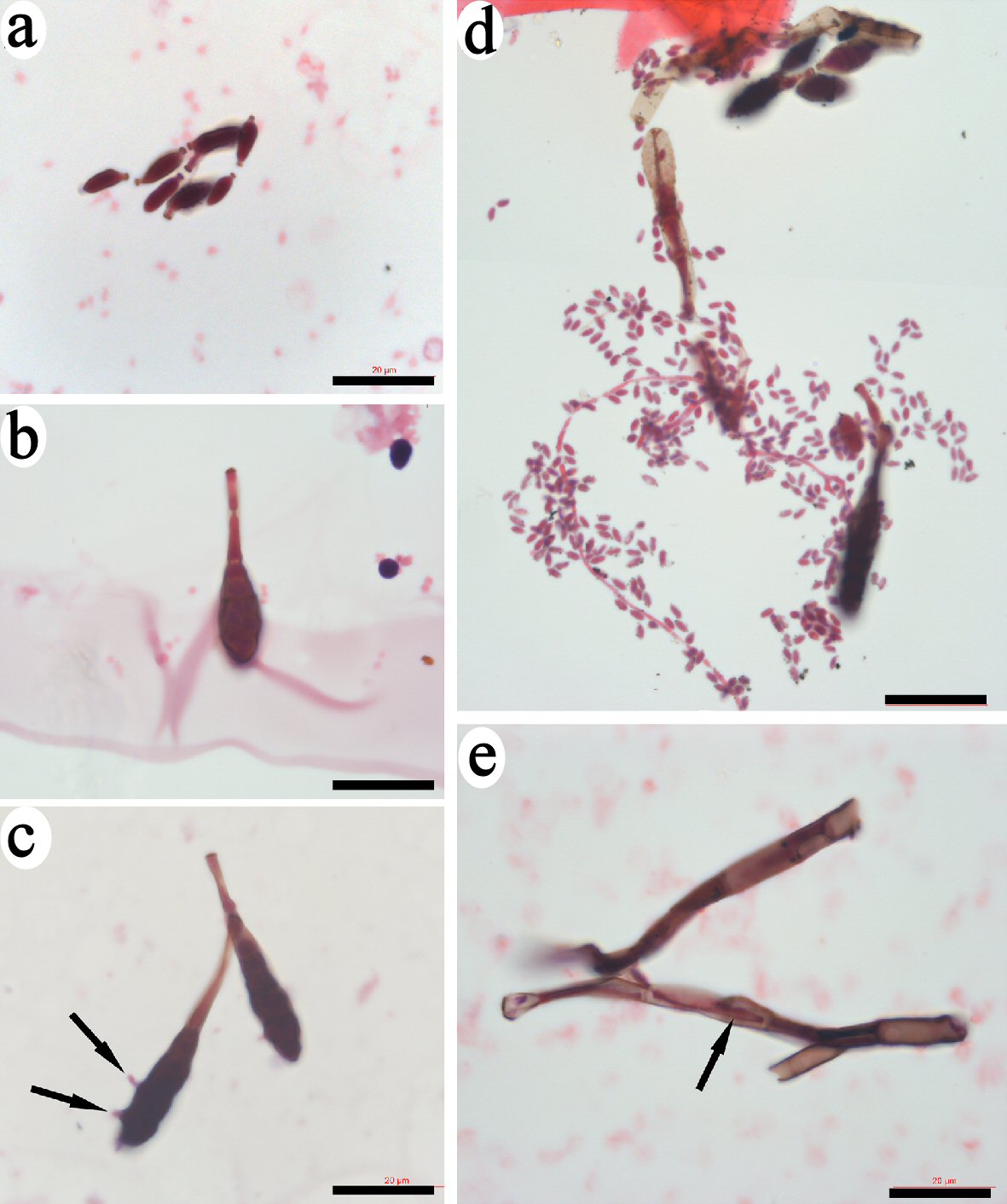
Figure 6. Identification of bud-like structure that released spore-like progenitors. Small bud-like structures of less than 10 µm that had similar morphologies and were stained copper-color were identified (a). Some larger-sized bud-like structures that contained dark inclusions were identified (b, c). Few small progenitors extruded through the membrane of bud-like structure (arrows in c). The leaf-like membrane of the bud-like structures opened to release numerous small spore-like progenitors (d). Bars = 20 µm.





