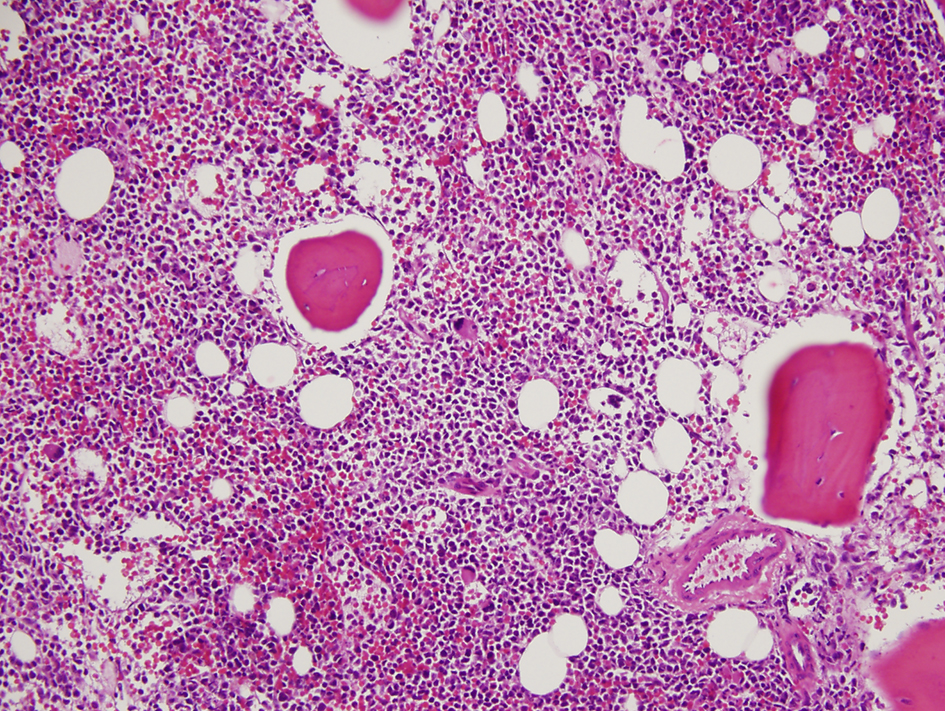
Figure 1. Hypercellular bone marrow with myeloblasts (× 20 magnification).
| Journal of Hematology, ISSN 1927-1212 print, 1927-1220 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Hematol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.thejh.org |
Case Report
Volume 6, Number 4, October 2017, pages 96-100
A Case of Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia in a Patient With Heterozygous Mutations in the Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated Gene
Figures

Table
| Topoisomerase II inhibitors (e.g. doxorubicin) | Alkylating agents (e.g. cyclophosphamide) | |
|---|---|---|
| Onset of t-AML | 2 - 3 years after exposure | 4 - 7 years after exposure |
| Pre-leukemic phase | No preceding myelodysplastic phase; frequently presents as overt acute leukemia often with monocytic component | Patients may present with MDS or AML with myelodysplastic features |
| Cytogenetic abnormalities previously documented | Translocations to 11q23 Translocations to 11p15 Translocations to 21q22 Translocations to 16q22 inv(16)(p13q22) t(15;17)(q22;q12) t(11;16)(q23;p13.3) t(8;21) t(9;11) | Deletions or monosomy of chromosome 5 or 7 t(3;21) |
| Prognosis | Similar to cases of de novo AML with corresponding genetic abnormalities | Worse than de novo AML |