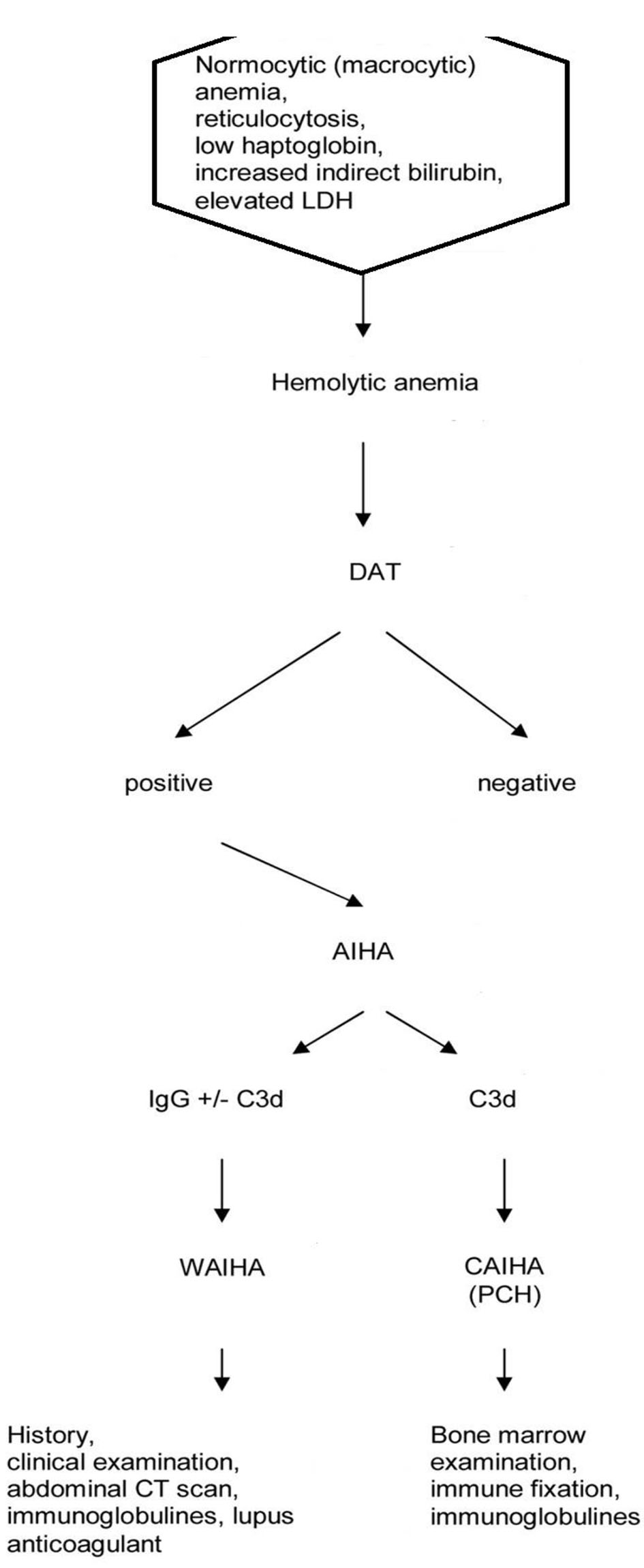
Figure 1. Flow chart of diagnosis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
| Journal of Hematology, ISSN 1927-1212 print, 1927-1220 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Hematol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.thejh.org |
Original Article
Volume 6, Number 1, March 2017, pages 12-20
Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Clinical Profile and Management
Figure

Tables
| Underlying disorder | Prevalence of AIHA | wAIHA | cAIHA | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NHL: non-Hodgkin lymphoma; SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus; CVID: common variable immune deficiency; ALPD: autoimmune lymphoproliferative disease; SCT: stem cell transplantation. | ||||
| CLL | 2.3-4.3% | 87% | 7% | [24, 25] |
| NHL (except CLL) | 2.6% | More common | Less common | [26] |
| IgM gammopathy | 1.1% | No | All | [27] |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 0.19-1.7% | Almost all | Rare | [28] |
| Solid tumors | Very rare | 2/3 | 1/3 | [29] |
| Ovarian dermoid cyst | Very rare | All | No | [30] |
| SLE | 6.1% | Almost all | Rare | [31] |
| Ulcerative colitis | 1.7% | All | No | [32] |
| CVID | 5.5% | All | No | [33] |
| ALPD | 50% | All | No | [34] |
| After allogeneic SCT | 4.4% | Yes | Yes | [35] |
| After organ transplantation | 5.6% (pancreas) | Yes | No | [36] |
| Drug-induced in CLL | 2.9-10.5% | Almost all | Rare | [37] |
| Interferon α | Incidence: 11.5/100,000 patient-years | All | 0 | [38] |
| Characteristics | Primary wAIHA | Secondary wAIHA | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Females | 12 | 26 | > 0.05 |
| Males | 17 | 20 | > 0.05 |
| Mean age at wAIHA onset in years | 51.7 ± 20.5 | 54.3 ± 25.7 | > 0.05 |
| Clinical features at the time of onset, n (%) | 27 (93.10%) | 31 (67.39%) | > 0.05 |
| Anemia, n (%) | 21 (72.41%) | 29 (63.04%) | |
| Jaundice/dark urine, n (%) | 11 (37.93%) | 15 (32.60%) | |
| Chest pain/ACS, n (%) | 3 (10.34%) | 5 (10.86%) | |
| Characteristics of patients at onset | |||
| Mean hemoglobin level at AIHA onset (g/dL) | 7.1 ±1.7 | 6.3 ±1.2 | 0.029 |
| Mean reticulocyte level at AIHA onset (× 109/L) | 323 ± 179 | 262 ± 156 | > 0.05 |
| Mean MCV level at AIHA onset (fL) | 109 ± 16 | 104 ± 18 | > 0.05 |
| Decreased level of haptoglobin (%) | 27 (93.10%) | 43 (93.47%) | > 0.05 |
| Increased LDH level (%) | 29 (100%) | 42 (91.30%) | > 0.05 |
| Increased Bilirubin level (%) | 25 (86.20%) | 39 (84.78%) | > 0.05 |
| DAT pattern | |||
| IgG | 15 (51.72%) | 15 (32.60%) | > 0.05 |
| IgG + C3d | 14 (48.27%) | 30 (65.21%) | > 0.05 |
| C3d | 0% | 1 (2.17%) | |
| IgA | 0% | 2 (4.34%) | |
| Treatment administered | |||
| Blood transfusion | 20 (68.96%) | 34 (73.91%) | > 0.05 |
| Response to corticosteroid (%) | 28 (96.55%) | 40 (86.95%) | > 0.05 |
| Dependence on corticosteroid (%) | 17 (58.62%) | 32 (69.56%) | > 0.05 |
| Complete response to corticosteroid (%) | 20 (68.96%) | 30 (65.21%) | > 0.05 |
| Second line treatment (%) | 19 (65.51%) | 32 (69.56%) | > 0.05 |
| Rituximab usage | 14 (48.27%) | 23 (50%) | > 0.05 |
| Splenectomy | 1 (3.4%) | 15 (32.60%) | < 0.05 |
| Disease remission at last consultation | 22 (75.86%) | 33 (71.76%) | > 0.05 |
| Complete remission of AIHA | 14 (48.27%) | 23 (50%) | > 0.05 |
| Partial remission of AIHA | 8 (27.58%) | 12 (26.08%) | > 0.05 |
| Active disease | 8 (27.58%) | 14 (30.43%) | > 0.05 |
| Venous thrombosis | 4 (13.79%) | 11 (23.91%) | > 0.05 |
| Deaths | 3 (10.34%) | 4 (8.69%) | > 0.05 |
| Characteristics | Secondary to lymphoma (N = 18) | Other forms (N = 58) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female patients | 11 | 27 | > 0.05 |
| Male patients | 7 | 30 | > 0.05 |
| Mean age of onset (years) | 69.7 ± 21.5 | 44.7 ± 23.2 | 0.012 |
| Clinical symptoms at the time of onset | 14 (77.77%) | 45 (77.58%) | > 0.05 |
| Investigations | |||
| Mean hemoglobin at onset (g/dL) | 6.4 ± 1.5 | 6.6 ± 1.8 | > 0.05 |
| Hypogammaglobulinemia, n (%) | 10 (55.55%) | 6 (10.34%) | 0.01 |
| Monoclonal gammaglobulin, n (%) | 13 (72.22%) | 10 (17.24%) | 0.0019 |
| Direct antiglobulin test (DAT) | |||
| IgG | 2 (11.11%) | 30 (51.72%) | 0.029 |
| IgG + C3d | 14 (77.77%) | 28 (48.27%) | > 0.05 |
| C3d | 9% | 0% | |
| IgA | 0% | 4% | |
| Treatment | |||
| Blood transfusion | 95% | 49% | 0.02 |
| Response to corticosteroids (%) | 94% | 90% | > 0.05 |
| Dependence on corticosteroids | 94% | 58% | 0.006 |
| Second line of treatment (%) | 96% | 51% | 0.005 |
| Rituximab | 64% | 41% | > 0.05 |
| Splenectomy | 5 (36%) | 5 (11%) | 0.04 |
| Disease remission at last visit | 57% | 76% | > 0.055 |
| Complete remission of AIHA | 5 (36%) | 23 (50%) | |
| Partial remission of AIHA | 3 (21%) | 12 (26%) | |
| Active disease | 6 (43%) | 11 (24%) | |
| Thrombosis | 2 (14%) | 7 (15%) | > 0.05 |
| Deaths | 3 (21%) | 2 (4%) | > 0.05 |
| B-cell lymphoma | 18 (39.13%) |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 9 (19.56%) |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 8 (17.39%) |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | 3 (6.52%) |
| Common variable immune deficiency | 2 (4.34%) |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 2 (4.34%) |
| Secondary to drug usage | |
| Alpha methyldopa | 2 (4.34%) |
| Carbamazepine | 2 (4.34%) |